Fundamentals of Governmental Accounting and Reporting Courses
Difference Between Fiat Money and Commodity Money
11 de mayo de 2022Silvesterfeuerwerk 2023 2024 Zuschlagen » Pyroweb De
12 de mayo de 2022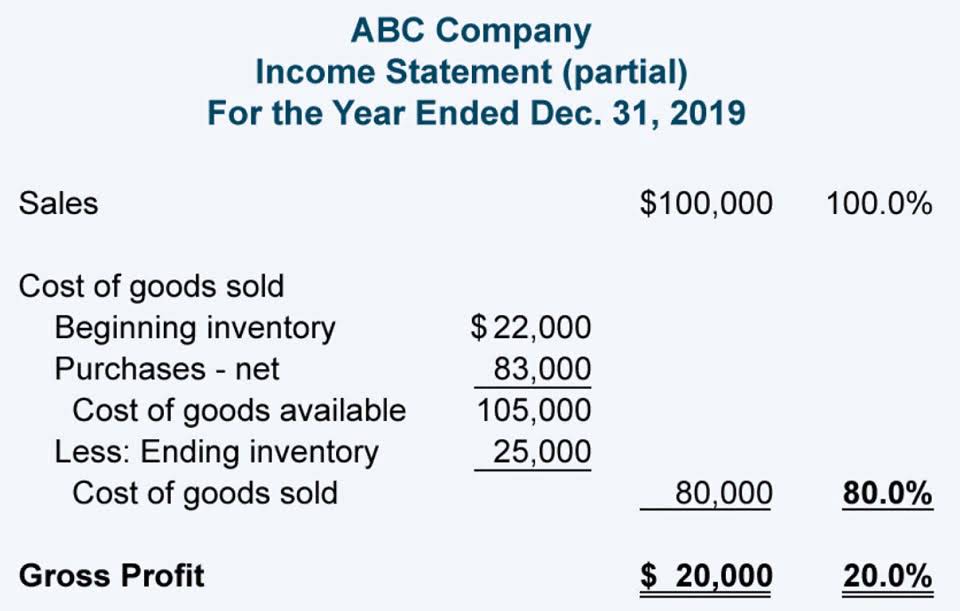
In turn, the GASB is funded primarily by accounting support fees paid by brokers and dealers who trade in municipal bonds. This funding mechanism was established by Section 978 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010. Appropriations for the U.S. federal government are decided by Congress through various committees. The U.S. government’s governmental accounting definition fiscal year runs from October 1 through September 30 of each calendar year. For a partnership, the primary purpose of the appropriation account is to show how profits are distributed among the partners. For an LLC, the appropriation account will start with profits before taxes and then subtract corporate taxes and dividends to arrive at retained profits.
- In some cases, professionals in government accounting jobs may earn more than their colleagues in other sectors.
- Various governmental accounting systems are used by various public sector entities.
- Additionally, transparency and accountability requirements are much higher in the public sector.
- Because government agencies serve as stewards of taxpayer money, using the money to provide valuable services and goods to the public, there is a need for both uniformity and transparency in the way that financial data is reported.
The sum total of these adjustments is referred to as the modified accrual basis. Under the modified basis of accounting, revenue and governmental fund resources (such as the proceeds from a debt issuance) are recognized when they become susceptible to accrual. This means that these items are not only available to finance the expenditures of the period, but are also measurable. The “available” concept means that the revenue and other fund resources are collectible within the current period or sufficiently soon thereafter to be available to pay for the current period’s liabilities. The “measurable” concept allows a government to not know the exact amount of revenue in order to accrue it.
Government Accounting Overview
There are many entities that oversee and monitor the government, such as elected officials, creditors, other governmental agencies, and people within the communities they serve. They do this by using fund accounting and following the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The majority of government agencies are funded at some level by funds received from various taxes or grants. Because government agencies serve as stewards of taxpayer money, using the money to provide valuable services and goods to the public, there is a need for both uniformity and transparency in the way that financial data is reported. Measurement focus identifies what financial transactions and activities will be documented in the financial statements.
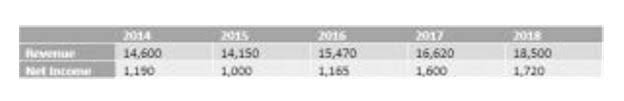
To clarify the difference between these concepts, the basis of accounting governs when transactions will be recorded, while the measurement focus governs what transactions will be recorded. Governmental accounting maintains tight control over resources, while also compartmentalizing activities into different funds in order to clarify how resources are being directed at various programs. This approach to accounting is used by all types of government entities, including federal, state, county, municipal, and special-purpose entities. Governmental accounting is the process of recording summarizing, analyzing, and reporting financial transactions incurred by a government. Also referred to as tax, accounting, or budget specialists, these compliance officers hold a strong knowledge of fiscal policy, laws, and regulations.
Fiduciary Funds
Government agencies are entrusted with the use of public funds for the good of their citizens. To help facilitate this, an independent organization known as the Government Accounting Standards Board, or GASB, was established to provide a set of accounting standards for governmental units. The focus of governmental funds is on current financial resources, which means assets that can be converted into cash and liabilities that will be paid for with that cash. Stated differently, the balance sheets of governmental funds do not include long-term assets or any assets that will not be converted into cash in order to settle current liabilities. Similarly, these balance sheets will not contain any long-term liabilities, since they do not require the use of current financial resources for their settlement.
- GASB is an independent, non-political entity that sets accounting standards for governmental units.
- The GASB creates and issues guidance to support quality financial reporting to assist independent analysts, investors, and others in understanding the complex financial transactions which take place in government.
- The GASB’s uses an open and independent process that encourages broad participation from all stakeholders and objectively considers and analyzes all their views.
- By effectively managing public funds, it can improve resource allocation, reduce wastage, and promote the responsible use of taxpayers’ money.
- Glassdoor reports a median annual salary of over $80,000 for federal government accountants — almost $6,000 more than the median for accountants in all industries.
- Given the unique needs of governments, a different set of accounting standards have been developed for these organizations.
Government accounting refers to the comprehensive process of recording, categorizing, summarizing, and interpreting all financial transactions incurred by the government. This process includes recording the government’s income and expenditures across various departments and projects. These branches of accounting, working together, aim to provide a crystal-clear financial representation of the public sector to ensure its accountability, efficiency, and transparency. Funds are used by governments because they need to maintain very tight control over their resources, and funds are designed to monitor resource inflows and outflows, with particular attention to the remaining amount of funds available. By segregating resources into multiple funds, a government can more closely monitor resource usage, thereby minimizing the risk of overspending or of spending in areas not authorized by a government budget.
How Appropriation Accounts Work
Proprietary funds use the economic resources measurement focus and the accrual basis of accounting. And fiduciary funds are reported similarly as proprietary funds, with an exception for the recognition of certain liabilities of defined benefit pension plans. The importance of public sector accounting cannot be overstated, as government agencies receive funds in the form of taxes and grants, and it is necessary to maintain uniformity and transparency while reporting the financial data. To show accountability to the people within the communities they serve, governments must provide financial data that is relevant, trustworthy, and understandable. To ensure this, the Government Accounting Standards Board (GASB) was established in 1984 to help governmental agencies maintain the needed uniformity and transparency. The GASB creates and issues guidance to support quality financial reporting to assist independent analysts, investors, and others in understanding the complex financial transactions which take place in government.

They apply that knowledge as they analyze documents and data to ensure regulatory adherence. Learn more about skills and specializations in government accounting, and discover how to start a career in the field. In accounting, it refers to a breakdown of how a firm’s profits are divided up, or for the government, an account that shows the funds a government department has been credited with. A company or a government appropriates funds in order to delegate cash for the necessities of its business operations. Advanced financial information systems and big data analytics can provide more profound insights into financial data, enabling better decision-making.
Understanding Government Accounting: A Comprehensive Overview
Internal auditors also analyze current documentation to advise government departments and agencies on best fiscal practices. Specializations, location, experience, and education can affect an accountant’s earning potential. With experience and education, internal auditors can move from entry-level positions to more advanced roles. Positions like intermediate, senior, and chief internal auditor often come with increased earning potential. The GASB is subject to oversight by the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF) Board of Trustees, which selects its board members, and the FASB, both of which it funds.
